On Episode 062 of the Your Financial Pharmacist Podcast, Tim Baker, owner of Script Financial and YFP Team Member, and Tim Church, YFP Team Member, talk about the ‘other’ forgiveness through the federal loan system. Many borrowers aren’t aware that this program exists, so Tim and Tim spend this episode shining a light on the details of the program and who should consider it.
Mentioned on the Show
- YFP Student Loan Refinancing Resources
- Script Financial
- YFP Facebook Group
- YFP Episode 018: Maximizing the Benefits of Public Service Loan Forgiveness
- YFP Student Loan Course
- YFP Blog: Defining and Calculating Discretionary Income for Student Loans
- Set Up a Taxable or Brokerage Account
Episode Transcript
Tim Baker: What’s up, everybody? Welcome to Episode 062. I am here with my co-host, Tim Church. We are going to talk all about the ‘other’ loan forgiveness program. Tim, I’m excited to be here with you. What’s going on?
Tim Church: Hey, Tim. Glad to be be back on and excited to hear that you and Tim Ulbrich are going to be heading down to south Florida coming up in a couple months.
Tim Baker: Yeah, this will be our — so I think Tim and I just booked our flights. We’ll be down for our T3 conference to talk Your Financial Pharmacist business in West Palm Beach, Florida. I think it will be our first meeting there, so we’ll finally be able to meet Andrea, and you’ll be able to not travel for one of our meetings for once, right?
Tim Church: Exactly. And I’m not going to have to go into the snow, and you guys are going to have to bring beach attire. Get ready to go.
Tim Baker: That’s true. I can work on my base tan. Yeah, so today, Tim, we’re going to talk about — you know, we talk, obviously, student loans a lot on the podcast, but we’re going to talk a little bit more about the non-PSLF forgiveness program, which a lot of people don’t know is a thing. So you know, I’m interested to kind of talk with you and kind of we’re going to take a more casual approach, I think, and just talk about the program and some of the details behind it. But what are the — I guess for you, what do you think are some of the reasons why, you know, people or pharmacists come out, and they don’t, they’re not aware of I guess some of the strategies that are out there. Why do you think that is?
Tim Church: Well, I mean I think we’ve talked about it many times that not every school is going to put personal finance in their curriculum and make it a priority. And some schools, they have it as an elective. But really, the bare minimum that students have is as they come out and as they graduate is they have the exit loan counseling, which as I think we heard from many people that that’s just not enough. It’s just such a small amount of information that they get, and so it’s really hard to sort of cram everything in there that you need to know about your loans. And with so many repayment plans and structuring and different dates and eligibility, I mean, it can be very overwhelming to kind of understand and know first of all, your options, but then all the nuances within all of those options.
Tim Baker: Yeah, it’s funny. I had a meeting with a resident, so I work with some students and some residents, and we were talking about her loans. And I was asking her what her strategy was, and we’ll break down the difference between strategy and repayment plans and things like that. And you know, she was kind of in this deferral period. I was looking at kind of some of the questions that I was asking, I was like, man, we need to switch this up. And I asked her about like had she considered forgiveness or PSLF, and she didn’t even really know what PSLF was. And you know, I think sometimes when I look at our Facebook group, and I see some of the conversations there, there’s a lot of people out there that are kind of in-the-know with their student loans, and I think they understand the different strategies and the plans available to them. But I think that there are also some that don’t know. And for this particular case, we’re talking $200,000 in loans. It’s a big deal. So I think having all of the different strategies and repayment plans kind of in front of you is important, and really breaking those down is important because, you know, you can make decisions, you know, in residency or as a new practitioner that are going to affect really the next 10-20 years of your life. So I think it’s important to kind of talk through those. So let’s talk about that, Tim. When we’re talking a student loan strategy versus a repayment plan, what are we talking about here?
Tim Church: Yeah, that’s a great point. And I think so many people get these two things confused because repayment plans, really, they’re going to dictate your minimum payments over a designated term, and that really could be in the federal system, could be a refinance, but basically, you have a set plan that says how much you’re going to have to pay a month and at least over a minimum period of time. But when you’re talking about a strategy, you’re really looking at your comprehensive game plan on the most effective way how you’re going to tackle your loans. And really, for most people, it’s going to be, well, what’s the strategy or game plan that’s going to save me the most money? And really, that strategy could be executed using a number of different repayment plans, especially if someone is going to keep their loans in the federal system and pay them off that way or whether they’re pursuing one of those forgiveness programs. So one of the things that we’ve kind of talked about is when you kind of look at very broadly, if you’re looking at your student loans, what are those main strategies that you can kind of look at and analyze? And really, for a lot of people, they’re going to be looking at really three different broad strategies. So the first one — and we always talk about this because a lot of people are unfortunately not eligible, but it’s great if you have it, is tuition reimbursement programs. So a lot of those are through the federal government, through the Veterans Affairs, Indian Health Service, Public Health Service, National Institute of Health, so there’s great programs that exist, just unfortunately, there’s not a lot of people and not always everyone is eligible because that’s essentially free money that your employer is giving you or matching you. And then so to the next big, broad kind of strategy is non-forgiveness, so everything that’s outside of the forgiveness realm. That could be refinancing your loans through a private lender or it could be keeping your loans in the federal system and just paying them off through one of the repayment plans. And then besides that, really you have forgiveness, and that can even break down, and that’s where we were kind of going with the Public Service Loan Forgiveness or what we would call non-PSLF forgiveness or the ‘other’ forgiveness.
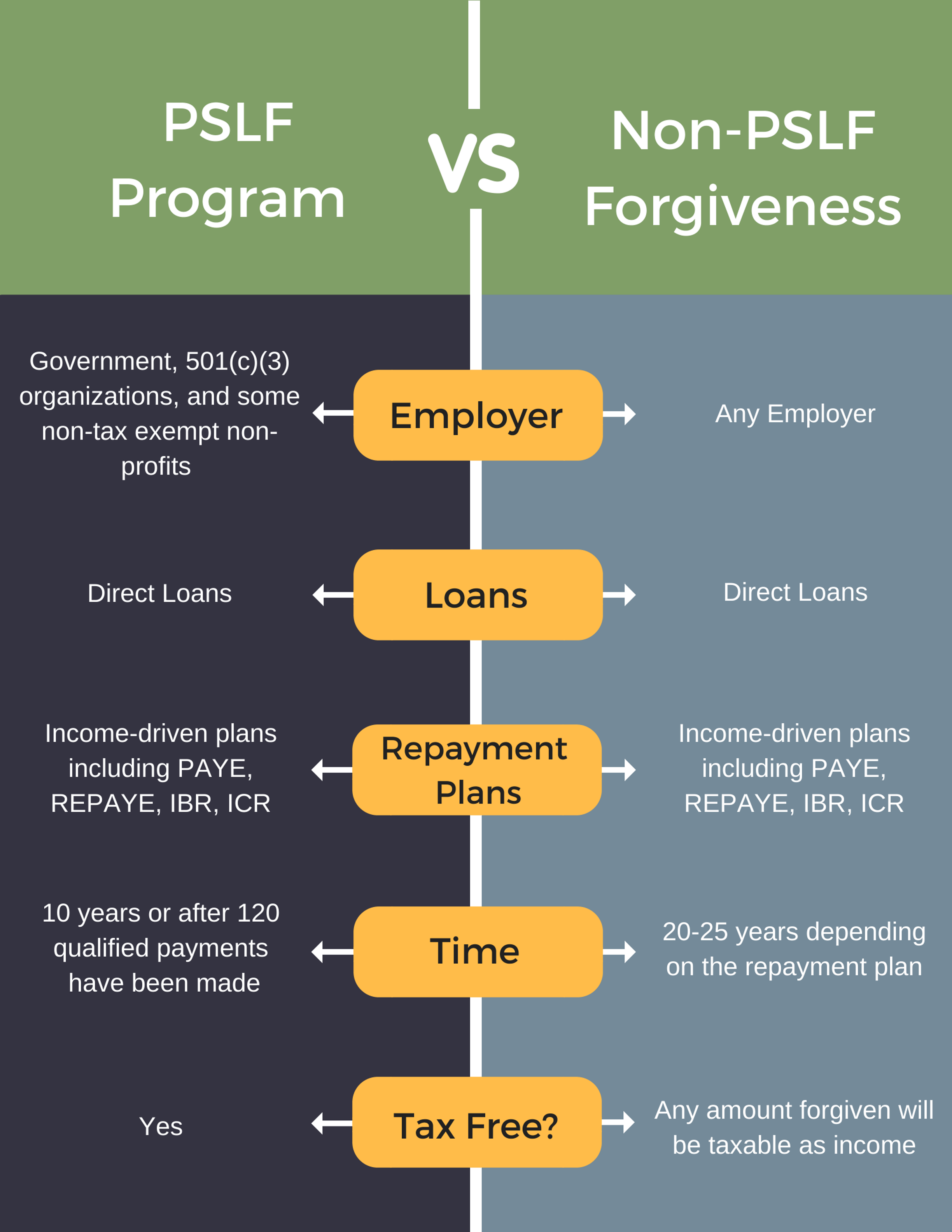
Tim Baker: So when we say the non-PSLF forgiveness — so I guess to break that down a little bit, you know — so let’s first talk about, why don’t we first talk about PSLF, and we’ll just kind of walk through that. So you know, typically, when I talk with clients, and I’m looking at their student loans, typically kind of the rhythm of this is that they have to work for a certain type of employer, like you mentioned. And typically, that is a 501c3 nonprofit. So if you don’t know if your company’s a nonprofit, there are different resources out there that you can check it out and see if they are. You have to have the right type of loans, so that’s typically the federal loans that we’re talking about. You have to be in the right type of repayment plan, which is typically one of the income-driven plans, so the ones you’ve heard of, which are IBR and ICR, and then the newer ones on the block are pay-as-you-earn and revised pay-as-you-earn. You have to make the right amount of repayments, so in the PSLF, it’s 10 years. Those have to be consecutive, you’re basically looking at 120 payments. And then you prove it, and you typically do that with your employment certification form. And then when you do that, you apply for forgiveness, and you receive tax-free forgiveness. So that’s kind of the way it works, and like I said, we’re not going to spend too much time on PSLF, but — I don’t know, Tim, should we kind of talk about some of the updates now in terms of that program? And then we can kind of shift to the non-PSLF forgiveness?
Tim Church: Yeah, I mean really, not much has changed. There’s still the questions that are on the table about the uncertainty on the longevity of the program — you know, will it be capped at a certain level? Will it still exist in the future? I’ve kind of been searching off-and-on on the Internet to see how many cases of people that have been actually received forgiveness, and really, I still only see just a few out there.
Tim Baker: Which is amazing. It’s amazing when you think about it because of the problem — whoever is running PR for like the PSLF or fed loan servicing really kind of needs to look in the mirror because it has such a bad reputation, but I know it’s happening. We don’t know, but when we were making this student loan course, I called fed loan servicing just to kind of get an inside opinion of where PSLF is going, and you know — to kind of give a little bit more background on what PSLF is, it was put in place when George W. was in office and then basically, both administrations then, both Obama and the current administration under Trump either talked about capping it or eliminating it completely. So there is some risk to that. I think what is comforting in some regards is in March, which is probably the most recent news when it comes to the forgiveness program is that the Congress has allocated $350 million for those that were seeking forgiveness that didn’t quite line up everything for them to be in forgiveness. And actually, I just read an article from Forbes, who this lady was, I think she was like eight years into forgiveness, but she had FFEL loans, and FFEL loans, unfortunately, are not eligible for forgiveness. You have to actually consolidate those first, so — and I actually have a client that’s kind of going through the same thing. She was halfway through forgiveness, and not all of her loans were in the right type of loan, so she essentially has two different clocks, one that was in the correct type of loans, and one that wasn’t. So the point being is that Congress, the government, has allocated some funds for those, mistake cases that in all intents and purposes, they should be forgiven. So there’s that. Now, to shift gears here and kind of talk about the non-PSLF forgiveness. So if we kind of use the same type of rhythm in talking through non-PSLF is don’t — in terms of the right type of employer, it doesn’t matter who you work for. You could work for the circus and still receive non-PSLF forgiveness. So it doesn’t matter if your employer is a nonprofit or not.
Tim Church: Are there pharmacists in the circus, Tim? I wasn’t sure. Is that some of your clients that are in there?
Tim Baker: I think some of them either they feel like they’re working in the circus or they want to work in the circus.
Tim Church: Oh, OK.
Tim Baker: So sometimes, that’s the case. But let’s say we’ll keep it positive here, so it doesn’t matter who the employer is. They still need to be in the right kind of loan, so this is your federal direct loan. So again, no private loans can be forgiven here. They still have to be in the right type of repayment plan, so that’s one of the four income-driven plans. And they have to make the right amount of payments. Now, this is typically over 20 or 25 years instead of the 120, so this is the 240 payments over 20 years or 300 over 25 years, depending on what type of repayment plan. You don’t really have to prove it, you still have to re-certify your income every year, which is going to basically change your repayment, and then you apply and you receive forgiveness. Now, what’s left out of there that you heard me say with PSLF is that with PSLF forgiveness, it’s tax-free forgiveness. In the non-PSLF program, it’s taxable forgiveness, so what does that — Tim, what does that mean when I say taxable forgiveness?
Tim Church: So essentially, any amount of money that you have left at the end, any balance remaining on your loans at the time of forgiveness, the IRS basically treats that as income. So whatever you make 20 and 25 years down the road, your income from the previous year plus whatever amount is going to be forgiven will be tacked on as income. So essentially, you would be responsible for paying any of the taxes for that. And I think we’re going to break that down in a little bit more detail later on in the episode. But I want to kind of shift back to what you were talking about in terms of the years, in terms of the repayment period. So you’re kind of talking about you’ve got to have direct loans, you have to be in an income-driven payment plan, and actually, you can also be in a standard repayment plan actually counts, which doesn’t really make much sense. If you were in the standard repayment plan, you’re on track to pay it off in 10 years. But in case you started out in the standard plan, you could have made payments and then shifted over. But those would still count if you shift later, at a later point down into an income-driven plan. But when you looked at the different income-driven repayment plans, that’s where the timeline is a little bit different. So if you look at the revised pay-as-you-earn or re-PAYE, really it comes down to whether your loans are all undergrad or whether they’re going to be professional. So we’re talking for pharmacists, most of those are going to be for professional study, most likely. So if you have any loans that are for a graduate or professional degree, that timeline is going to be 25 years. So basically, you have to make those 300 payments over that timeframe in order for those to count. Now, and contrast that with the pay-as-you-earn or PAYE, that’s going to be a 20-year period. So the same thing will be true if you’re in the new IBR, or income-based repayment plan, it will also be 20 years — so if you’re a new borrower on or after July 1, 2014. And then for the old IBR, or the ICR, income-contingent plan, that’s going to be a 25-year repayment period.
Tim Baker: Who ultimately should consider this strategy when we’re viewing their student loans? Because like, you know, I hear a lot of, you know, I hear a lot of kind of chatter of, you know, looking at, you know, extended or extended graduated repayment plans that are out there, and which way to go in terms of, you know, if you’re not eligible for the PSLF program. So who ultimately should look at this program?
Tim Church: It’s a great question. And I mean, even just to kind of take a step back and think about it, like who wants to be in debt for 20-25 years? That’s a long period of time when you think about it. But I think there are some cases where it’s definitely something that you have to consider. There’s no perfect example of this, but I think the people that we’ve talked about quite a bit in the course and going through that is if you have a very huge debt-to-income ratio, so we’re talking at least 2-to-1. So for example, your income is $120,000, but you have student loans of $240,000 or more, then maybe this is something that’s on the table. And I think the reason that it becomes something that’s on the table is that if you start to look at the 10-year repayment for somebody with just massive student loan debt, I mean, that can be a huge chunk of your income every month, I mean, just to be able to make that payment. And then not only that, when you look at your other obligations, if you have other debt besides student loans or you live in a high-cost area, you know, that could be something that’s very difficult to do to even make that. And then you could say, well, what about refinancing to an extended period as well? And depending on how big the loan is, I mean, that can also be pretty difficult to pay. And again, if you’re extending that out for 20-some years, well, if you can get part of the forgiveness benefit, then you have to sort of look at that as being a potential option.
Tim Baker: Yeah, so whenever we talk about student loans, I always hearken back to the student loan course because I think one of the best things about the course is the decision table. So you basically, you look at your standard, the best repayment plan for non-forgiveness and non-PSLF forgiveness and PSLF forgiveness. And obviously, if one of them isn’t on the table, the PSLF, you cross that off. But it shows you very deliberately, you know, how long you’re going to — what the term of the loan is and what your total payment estimate would be after that. And the math, you know, the math typically doesn’t support any of the extended standard repayment plans. You’re either going to be looking at a standard plan or, depending on your strategy, looking at one of the two newer income-driven plans. And you know, the borrowers that have that larger debt-to-income ratios, anything that, like you said, Tim, is above 2-to-1, this would be something to consider. But the other thing that you have to really worry about is that tax bomb that comes at the end of that 20 or likely 25 years. So you know, if you have $100,000, which in some scenarios, that will definitely project out, that means that $100,000 that’s forgiven will be taxed. And if your taxed at a 25% income tax rate, then that’s a $25,000 tax bill, which is a little bit of a kick in the pants, you know, considering that you just were in debt for 20-25 years, and now you’re paying a large tax bill again. So I mean, there are different strategies to save for that, but you know, this is really a case where, again, if you’re in that. But I think one of the things that I think we’ve talked about amongst the Tims is at what point do we really — and maybe some pharmacists are at this because they understand the math behind it, but at what point do we view kind of that nonprofit status for the employer as almost part of your overall benefit packet. So like as an example, if I’m a new pharmacist and say I’m carrying $200,000 worth of debt, and I have a job for a nonprofit that pays me $100,000, and I have a job at a for-profit that pays me $120,000, I don’t think that we can look at that as well, this one place is going to pay me $20,000 more. I think that we really need to be a little bit more reflective and say, OK, if I look at this in totality and I look at the fact that, you know, you can’t argue with the math — I know I said this before — you can’t argue with math. And I know Tim Church, like we did this with your loans in retrospect. You can’t argue with the math of the PSLF. So if you are a believer, kind of like I am, that PSLF does have a little, that the program has legs, I think we really need to consider that as part of it. Like I did a student loan analysis for an individual, she’s actually a lawyer, so a non-pharmacist, and she walked out of the meeting saying, you know, I need to get back. She was in a nonprofit sector as a lawyer. She’s like, I need to get back to that because there’s no way that I want this hanging over my head for 20 or 25 years, and I don’t want to pay the I think it was $80,000 — or not $80,000, maybe like a $50,000 tax bill. I don’t know, Tim, what are your thoughts on that?
Tim Church: Yeah, I think you’re absolutely right that you have to consider that. And I think that a lot of times, people don’t. They’re looking at just standard salary, standard benefits and kind of what they’re looking to do. But as you’re going through that job search and how you’re going, I mean, that certainly is part of it. I mean, are you going to be working for a 501c3 or government entity? And is this something that could potentially change the course of how you pay your loans off? I mean, it’s a big deal because we’re talking over a long period of time, but also you have to look at that opportunity cost. So if you don’t pursue the PSLF or don’t go after it, then you’re losing that opportunity to potentially put a lot of your money towards retirement and other things. And I think that’s actually one of the things I wanted to go back to is that somebody that has a very high debt-to-income ratio and is coming out and just could feel extremely overwhelmed and they’re thinking, how do I even make these student loan payments? How am I even going to make those? Even if I refinance, maybe it’s going to be a huge chunk of my monthly income and even if I did that, how am I going to start retirement account? How am I ever going to get a house? How am I going to fund my children’s, my kids’ education? So I think like when you look at those, put that on the table that it can be very, very overwhelming. But if you’re sort of in one of these programs, in the program of non-PSLF, and you say, I can make income-based repayments, then I think that’s actually important to talk about as well. So how are those income-based repayments, how are those calculated? And I recently just put out a post on the website on how to define and how to calculate it because it has a very specific definition when you’re talking about these income-driven repayment plans. But most of the plans, so if we’re talking about re-PAYE, PAYE or the new income-based repayment, it’s going to be 10% of your discretionary income. Well how is discretionary income calculated? Well, that’s going to be based on your adjusted gross income, and that’s going to be — you’re going to subtract that from the poverty guideline. So those come out every year and change based on inflation and are relatively — they’re the same for all states except Alaska and Hawaii.
Tim Baker: All the Lower 48.
Tim Church: Exactly. And then your spouse’s income is only counted if you file jointly in most of the plans and in re-PAYE, it’s regardless of how you file your taxes. But when you look at that, when you break that down, you know, those payments can No. 1, they can be more manageable, but just like we’ve talked about with PSLF that funding retirement accounts and things like that, you can actually lower your payments that you’re making towards the loans by taking advantage of some of the tax benefits that are available.
Tim Baker: Yeah, so essentially, what you’re saying is that there are a few ways, a few levers to pull to lower your AGI, your adjusted gross income, and what you’re essentially doing is you’re deferring money into things like a 401k or a 403b or an HSA or a traditional IRA that allows you to kind of pay your future self but also lower the AGI, which will lower your payment and then hence, maximize your forgiveness.
Tim Church: Yeah.
Tim Baker: Go ahead, Tim.
Tim Church: No, and I was going to say too, now, some people may be listening to that and say, Well, if I’m lowering my payments towards my loans, won’t I be having a higher tax bill at the end of the forgiveness period, so whether that’s 20-25 years, and part of that is true. The balance may be a little bit higher, but I think the other thing to keep in mind is, you know, we talked — what did you mention? A $25,000 additional tax liability, could be something greater, but you also have to think that wherever that money is going to be in 20-25 years, is really going to be eroded. So it’s kind of hard to think about, I think, in today’s value because 20-25 years, you know, if you have to cover an extra $25,000 of income taxes, that may not be as — that’s really not going to be as substantial as what it would be today.
Tim Baker: So this might be a good part to bring up, we had a question on the podcast, Melissa from Salsbury, right down the street for me, asked, “You quoted on one podcast that after x number of payments, that one might qualify for non-PSLF. I’ve been paying on-time and extra for 16 years, didn’t know if I might qualify or soon qualify.” She talked about what she — looked like she had some proceeds that she could use, that could apply extra towards paying off the loan. So Melissa, thanks for asking the question on the Facebook group. I would say that if you qualify for non-PSLF, so you’ve been paying for 16 years, it’s really going to depend if you are in direct loans, so if you have Stafford or FFEL loans, those might not have qualified. So essentially what I would do is, you know, just look at your loans and see how long you’ve actually been paying. Those 16 years, are they all for direct loans? And you could be very well close to a forgiveness where you can actually apply and seek forgiveness, but it’s going to depend on really what kind of loans you’re in and what repayment plan. Typically, you’re probably in an income-driven plan. I think the second part of this is if you’re seeking a forgiveness — and this is kind of where we talk about you’re either forgiveness or you’re not. If you’re in a forgiveness strategy, whether it’s a PSLF play or a non-PSLF forgiveness play, you never want to throw extra money at the loan because essentially, you’re almost flying in the face of your strategy. So if you’re a Tim Church, and you’re being super aggressive on paying off the loans, he wants to plow as much money toward that loan as humanly possible because he’s not seeking any type of forgiveness or anything of that nature. If you’re on the other side of the fence where you’re trying to pay the least amount towards the loan, you want to basically maximize your forgiveness. So you wouldn’t apply any extra savings or money to the loan. So in your case, unless you find out that you are not on track to be forgiven for that non-PSLF time period, you would take that $25,000 and apply it elsewhere, whether it’s, you know, to plus up your emergency fund or apply that towards retirement savings or something like that. So I wanted to call that out, it’s really going to depend on your situation. So hopefully that answers your questions, but thanks for asking it. So what else, Tim Church? What else should we cover with regard to the non-PSLF forgiveness play.
Tim Church: Well, I honestly think if you’re really considering this option, I mean, one of the things I probably — if I were someone that was saying, this may be an option for me, a good play, I would really seek the help of an accountant. And the reason I say that is because No. 1, you have to think about the tax implications later on down the road. But you also have to think about what repayment strategy you should be in. And the reason that comes into play is we talked about that whether you have a spouse is going to depend on what kind of payments you’re going to make based upon that strategy and how you file your taxes. So really, it comes down to the repayment plan but also how you file your taxes and then preparing for that. So there’s a lot of different factors that go into the calculations, so I think having someone really go through and crunch the numbers and make sure that you’re on the right path that’s best for you, I think is really, really important. And then I think the other thing talking about is, OK, you’ve kind of said, OK, I’m comfortable with that tax bill coming up in 20-25 years. Well, how do you actually prepare for that? And you know, we’ve kind of talked about — you and I have before, that really, you know, there’s a couple different ways to go about it. One is you could just put money in a savings account and just have enough money for when it’s time to pay that extra taxes. But you know, why is that not a good idea, Tim?
Tim Baker: Typically, it’s not a good idea because you have such a long runway that, you know, if you — even right now, a lot of the better savings accounts out there are paying — they’re paying decent, you know, 1.5-2% interest, which is the highest it’s been in a long time. If you kind of believe in my philosophy, which is over long periods of time, the stock market will take care of you. And this is like 10+ years, so this would be 20-25 years. If you believe that over long periods of time, the stock market will take care of you, then you really should be investing your money there because you’re not going to touch it. Same thing with, you know, a lot of younger professionals with their retirement funds, you’re not going to touch it for a long, long time, so the market could go up and down and left and right, and so in a similar example, if you’re looking to build wealth for the potential tax bill that’s out there, I think some type of low-cost index fund is most appropriate to, you know, pay off the minimum amount of your student debt and then to put, you know, we’ve got to calculate it out, but to put a sum per month that you’re just buying into the market and letting it do its thing over time.
Tim Church: And so that should really be a separate account versus the retirement. You know, we were talking about —
Tim Baker: Exactly.
Tim Church: You can lower your AGI, and you definitely want to be saving for retirement over a 20-25 year period. But that’s probably not the best way to save for the tax implications because you could have penalties and other implications, and so really, you kind of have a separate type of investment account that you’re really designating for the tax bill. And one of the other things that I have actually heard come up in some political discussions is that that tax bill, there’s a potential that they could even eliminate that at some point. Now, obviously, that would be a good thing if you were saving and preparing for it all those times and then all of a sudden, the government said, ‘Hey, you know what, you actually don’t have to pay the extra taxes.’ I mean, that could be a great thing. But along the way, you’re doing the savings anyway.
Tim Baker: Yeah, and actually, you know, if listeners are interested in opening up that type of taxable or brokerage account, we actually put a link, you can open one up at Script Financial and fund it within like 15 minutes. So we can do that. But essentially, those types of accounts are, they’re not retirement — most retirement accounts if you take them out before 59.5, you have a penalty. This is essentially, you know, it’s like a savings account, but you can actually invest it. And that’s the idea. To kind of talk about that, yeah, there is some conversation about allowing all forgiveness to be tax-free, not just the Public Service Loan Forgiveness. And I think that could be an option. That definitely could be an option. I think to kind of circle back on the longevity of the program, I think it’s — it is a very political thing. I think it’s easier to eliminate the non-PSLF program, which is what we’re talking about today. I think it’s easier politically to do that, so I think if you start seeing things, forgiveness programs kind of be chopped, I think the non-PSLF would go first before the PSLF. So yeah, so I think — could they do that, where it’s, you know, it is tax free forgiveness? Yeah, they could. But then they could also say, ‘We’re going to keep PSLF, but we’re going to completely eliminate the non-PSLF,’ because you know, from a political standpoint, you know, it’s hard to say, ‘Hey, I’m a teacher or I’m a doctor, I’ve been paying into this program for eight years, and now you’re going to pull the carpet out,’ versus whatever profession. So that’s just kind of my thought is there’s a lot of ways this could go. Again, if you are uncomfortable with having the debt hang over for 20-25 years, or you’re really uneasy about the longevity of either the PSLF or the non-PSLF, you know, this wouldn’t be something that you would necessarily want to pursue. But I think again, the situation, you know, math-wise, especially if you have a higher debt-to-income, it’s going to be one thing you should at least consider to look at.
Tim Church: Alright so Tim, good work. I think we covered a lot on the non-PSLF forgiveness program. So just to kind of recap what we talked about here, so typically, this particular program is really for individuals or borrowers that they don’t have access to the PSLF program, typically this would be for someone that has a higher debt-to-income ratio, but the things that are similar across the board here is that in the non-PSLF, it doesn’t really matter who you work for. You want to make sure that you are in direct loans, those federal direct loans, that you’re making your 20-25 years worth of payment, most likely with PharmD’s, it’s going to be 25 years worth of payments in the re-PAYE, and that you are kind of certifying your income every year. And then at the end of it, you apply for forgiveness, and you receive taxable forgiveness. You have to worry about that tax bomb. So ultimately, lots of risks that play into this particular forgiveness program, but I think given those particular set of borrowers, it does make sense to at least consider. So Tim, good to have you on this episode as co-host and looking forward to next time.
Tim Baker: Thanks, Tim.
Join the YFP Community!
Recent Posts
[pt_view id=”f651872qnv”]







