Rapid Fire Home Buying Q&A
On Episode 067 of the Your Financial Pharmacist Podcast, Tim Ulbrich, Founder of Your Financial Pharmacist, is joined by Nate Hedrick, the Real Estate RPh, to wrap up the month long series on home buying by taking questions from the YFP Community in a rapid fire Q&A format.
Summary of Episode
Nate Hedrick answers questions from the Your Financial Pharmacist community covering various facets of home buying process. Nate shares advice, resources, and parts of his financial, real estate, and home buying journeys to help answer these questions. The first question asks how to save for a down payment. Nate recommends using a savings account if the home will be purchased soon, otherwise he suggests to use a higher interest rate investment. The second question is in regards to comparing rates from different lenders without committing to them. Nate shares that it’s best to be upfront with lenders upon your initial conversation and let them know you are shopping around for a mortgage lender. During this process, you’ll receive a GFE (Good Faith Estimate) which is a document you can use as a comparison tool. Question three asks about tax advantages for home buyers. Nate discusses potential tax advantages for home buyers, such as buying down the rate or mortgage points, as well as property taxes. When asked about the process for building a home, Nate suggests asking pointed questions to the builders and to be wary of perks and additional up-sells they may pitch. Nate then talks about real estate crowdfunding sites which pull money together from different investors to leverage larger investments. Finally, Nate discusses buying a home while in debt with student loans.
About Today’s Guest
Nate Hedrick is a 2013 graduate of Ohio Northern University. By day, he works from home as a hospice clinical pharmacist for ProCare HospiceCare. By night, he works with pharmacist investors in Cleveland, Ohio – buying, flipping, selling, and renting homes as a licensed real estate agent with Berkshire Hathaway. This experience has led to a new real estate blog that covers everything from first-time home buying to real estate investing. Nate’s blog can be found at www.RealEstateRPH.com
Mentioned on the Show
- Splash Financial
- Real Estate RPh
- YFP Concierge Service w/ Nate Hedrick
- YFP Episode 064: 6 Steps to Home Buying (Part 1)
- YFP Episode 065: 6 Steps to Home Buying (Part 2)
- YFP Episode 066: 10 Home Buying Lessons Learned
- Home Buying Quick Start Guide
- YFP Episode 56: Rapid Fire Student Loans Q&A
- YFP Episode 61: Rapid Fire Insurance Q&A
- YFP Facebook Group
- Ally.com
- Script Financial
- YFP Episode 009: Interview with Carrie Carlton
- Rich Dad Poor Dad: What the Rich Teach Their Kids About Money That the Poor and Middle Class Do Not! by Robert T. Kiyosaki
Episode Transcript
Tim Ulbrich: Welcome to the Your Financial Pharmacist podcast. This is Tim Ulbrich, and I’m excited to have again Nate Hedrick, the Real Estate RPH, back on the show to do a rapid-fire Q&A to wrap up this month-long series that we’ve been doing on home buying. So Nate, welcome back to the show.
Nate Hedrick: Hey, thanks for having me again.
Tim Ulbrich: So for our listeners, we’ve been all over this topic of home buying during the month of September. And if we have anybody listening who’s just jumping in at the end of this series, I’m going to quickly recap where we’ve been before we jump into the Q&A because I think that will help set the stage and hopefully give you an opportunity to go back and listen if need be. So here we are in Episode 067, and at the beginning of the month in episodes 064 and 065, Nate and I covered the six steps of the home buying process. And I think for those that are just getting started or want a refresher on home buying, that’s a great primer, and I’d highly encourage you to go back and check out episode 064 and 065. In 064, we cover three steps. In 065, we cover three more in detail. And then in Episode 066, last week, I talked through 10 home buying lessons that I have learned over the past few months, maybe some hard lessons, mistakes, lessons reinforced as my family gets ready to make the move from northeast Ohio to Columbus. And just as a reminder, along with this series, we have developed a YFP first-time home buying quick start guide that you can download for free at YourFinancialPharmacist.com/homeguide. Again, that’s YourFinancialPharmacist.com/homeguide. Nd if you’re looking to buy or sell or home or you want to get started in real estate investing or you just have a question that you want to have answered by a licensed real estate agent that is also a pharmacist, head on over to YourFinancialPharmacist.com/realestaterph, where you can get in touch with Nate, the Real Estate RPH. So Nate, you ready to do this rapid-fire Q&A?
Nate Hedrick: I’m ready. I’ve got my coffee, so I’m good. Let’s do it.
Tim Ublrich: Me too. I’m ready to go. So an early morning, here we go. And here’s the format. We’ve done several of these before. We’ve done one on student loans, insurance, and just like those, we’ve taken questions from the YFP community via email, via our Facebook group, and I’m literally going to throw them off one-by-one to Nate, and we’re going to hammer some of these. And then if we have time, I’ve got a couple at the end that are ones that are of interest to me and I know that have been asked out there before. So first question, Nate, comes from Austin via the YFP Facebook group. He says, “What is the best vehicle for saving towards a home purchase? Putting 20% down means holding onto a significant amount of money until finalizing a home purchase? So do you feel it is best to invest that money or save it in a low-interest savings account?” What do you think, Nate?
Nate Hedrick: Yeah, that’s an awesome question, Austin. So it’s funny, I’ll tell you the safe plan. And I’ll tell you what I did. The best bet is honestly to put that in a high interest savings account or some sort of rotating certificate of deposit, something that’s going to be able to basically meet or get near to inflation so that all those dollars you’re saving are basically protected and that your money is worth as much as it was when you put it in. Because if it takes you two or three or four years potentially to get that full 20% down, hopefully not that long, but depending on how long it takes, you want that money to be still worth as much as it was when you put it in. So the safe plan is a high interest savings account or a rotating certificate of deposit. But what we did when I was saving for our down payment, we didn’t have a high interest savings account. I think my savings account made .065% annually. It was a joke. So you know, I knew I was getting beat up by inflation every year that we basically didn’t pull the trigger. So what my wife and I did at the time was I took half of the money that we saved for a new home and put that in a savings account. And the other half for that down payment went into basically a short-term investment account. And I basically, the goal was to make about 6% on that investment, which isn’t outrageous. And if I could do that, basically and inflation was 3%, then I’m basically beating inflation with all that money. And so that was kind of the idea behind it. And it worked pretty well. It’s a riskier play, obviously, you can easily lose money that you’re investing, even in short-term investments, especially. So it’s a risker play. But again, at the time, I didn’t really have a whole lot of options. I suppose if I were just doing it today, I would look for some aggressive certificate of deposits, some of those online banks like Ally and whatnot are fantastic for that.
Tim Ulbrich: Yeah, and it’s nice that some of those higher yield savings accounts, the interest rate has come up a little bit, you know, so I think the last statement I got from Ally, it’s up towards 1.8% or something like that, which is nice from the .5%, .4%, .6% that we were living in. You know, to me, Nate, when I hear this question — and you alluded to this — I think about what’s the time horizon, what’s the appetite for risk? And then also just thinking about some of the tax implications and things along the way as well because if somebody’s looking at, you know, I really want to buy a home in six or 12 months, does the math on getting 6% in an account versus getting, you know, 1.5-2% in a savings account, you think about the potential risk that you’re taking out in an investment account versus a savings account, is it worth it with that time period when you really need the cash? Probably not. But if we have listeners out there that are thinking, you know, I’m in a position to start saving or maybe I have a gift from a family but I’m thinking about buying in five years or six years or seven years. When you think about that type of time horizon, to Nate’s point about the impact of inflation, I think that’s where you then start to think about, OK, how could I leverage these funds? Where yes, I’m investing them so they’re growing and beating inflation, but ultimately, I don’t necessarily want to be losing these moneys or at least minimize the risk of losing those moneys along the way. So for somebody that is thinking about investing, any other details you can provide? So you alluded to a little bit of a CD. When you talked about putting that money into a fund, were you just investing it in mutual funds out in the open market? Obviously you’re not doing that in a retirement account, I assume, correct?
Nate Hedrick: No, no. This was basically open market. Basically, you sign up with an online brokerage. I was doing individual stocks and bonds, I was doing larger investment vehicles like mutual funds, like you said, high dividend stuff. And obviously, like you said, there are tax implications to doing that. So this isn’t something you do lightly. But it’s something I had experience with and felt comfortable doing. And it was something that was, again, successful for me at that time. But I also had a larger time frame to look at. You know, we kind of started looking at that while I was still finishing up college, so I totally agree with you. If you’ve got a short-term play, you’re looking at a year, just throw it in a savings account, just protect that investment. And know that that money’s going to be worth it here in the next year, and you can use that down payment.
Tim Ulbrich: Yeah, and I think this is another good place too to think about, you know, the peace of mind variable, which often gets lost in the math and the weeds of this, right? So if you and/or a significant other or a spouse or somebody really wants to have the peace of mind that that money’s there and I’m not going to lose it, you’ve got to factor that into the equation.
Nate Hedrick: Definitely.
Tim Ulbrich: So Nate, I’m guessing some people are hearing this and thinking, 20% down? Do I really have to do this? I know we’ve talked about this on previous episodes, and you know, you do the math on this. On a $300,000 house, you’re looking at $60,000 down. On a $400,000 house, you’re looking at $80,000 down and so forth. And so we got a follow-up comment to this in the Facebook group where somebody alludes to, well, maybe you don’t need to put 20% down. So the comment here was, “I would consider weighing the option of not paying 20% down. Local credit union offers a first-time home buyer with 0% down. This avoids the PMI without having to save a boatload of money for down payment. Although credit scores were high, we were still approved, even with a pretty high student loan-to-income ratio. Keep in mind that the fixed rate was around 1% higher than going mortgage rate at the time. But with enough equity put in, we may explore refinancing to a lower percentage down the road if possible.” So we’ve talked before about in episodes 064 and 065, we talked a little bit about, OK, if you don’t have 20% down, you’re going to be paying Private Mortgage Insurance. However, there are some instances, and it looks like this is the case, where somebody’s not putting 20% down, and there’s no PMI, in fact 0% down loans. But the implications here are potentially a higher interest rate and obviously not having equity in the home. So what are your thoughts here and what are some variables for people to think about that may be leaning towards, you know what, I’m not going to put 20% down. What are your thoughts?
Nate Hedrick: Yeah. I think it all comes down to your priorities. You know, if your priority is to get into a home quickly, then yeah, I think it’s a really reasonable thing to not put 20% down. You know, before I started this financial journey, you know, our home, we didn’t put our full 20% down. We just got to the point where we had saved a good, I think we were at like 15%. And I said, look, this is the time, we’ve got to move. Our rental lease is up, and we just need a home for a couple of reasons. And so we just went for it. So it’s not for everybody, you kind of have to take that emotional side sometimes, which is harder to think about with a financial decision, and know that now, as we’re getting much, much further. We’re 10 years out now — well, almost 10 years out from the financial collapse of the housing market in 2008. There are a lot more options available to you now. I’m seeing a lot of 10% down conventional loans that have no PMI and the rates are pretty comparable. So there are products becoming more available. I think that the 20% down is very good in terms of being very financially stable and starting off with a lot of equity, but it’s by no means necessary.
Tim Ulbrich: Awesome. Next question comes from Mac via email. He says, “They say nowadays, your best off to obtain multiple loan quotes when buying a home. Sometimes it can be hard to compare rates when you are comparing apples to apples and fee structures, rates and commissions. What’s the best way to compare rates without going too far with one lender and then feeling committed to them? Or depending on how far down the road you are buying a home, is it too late to switch lenders and not put your purchase at risk in the market that we are in these days? What do you think?
Nate Hedrick: Yeah. That’s a great question. And there’s a couple aspects to it. So the first thing is I would go in with the expectation when you go to these lenders and tell them up front, I’m shopping around for a mortgage lender. My wife and I or my spouse and I or whatever are going to buying a home. And we wanted to find the appropriate mortgage lender for us. So help us make that to be you. And if you set that stage from the beginning, it’s going to be a little bit of an easier conversation. So they should be able to walk you down the road of OK, what kind of home are you looking for? What’s your budget? So on and so forth, which you have when you go in. And they should be able to give you a good faith estimate. This is a GFE document, it’s a very, very common thing. A good faith estimate shows you all of the numbers that they expect a loan to basically take. So an interest rate, it’s going to be all the fees, it’s going to be all the terms of that loan. So how long the loan is going to last, you know, are there prepayment penalties, are there escrow charges, what are the — all the aspects that go into the loan process. So that good faith estimate is that comparison tool because if you get three of those, one from each of your lender, although the individual loans may be a little bit difficult to compare, you’re going to have all that information in front of you, and you can do the math yourself to figure out how those stack up. So really once you get those good faith estimates, focus on the big numbers, APR or annual percentage rate, not just interest rate is a good way to do that. APR basically takes into account a lot of those fees. So if two loans are 4.5%, but one has $5,000 in fees and the other one has $0, that one with the fees is going to have a larger annual percentage rate, basically the effective interest rate is what they really should call it based on those fees that are built in. So you can use an APR to get a better estimate of what that loan is going to look like. The other big thing is you want to watch for — especially on your GFE — are things like rate locking and the ability to lock your rate at a certain time. That can be really beneficial. What the lender fees actually look like because these are one of the most negotiable aspects of a loan. You can basically take one lender’s fees and throw them at another lender and say, ‘Look, they’re not charging for this. I don’t think you should either.’ So that’s a good option. Watch for prepayment penalties. And then also watch for things like mortgage insurance. We’ve talked a lot about private mortgage insurance, but different loans require different amounts of it. And the GFE will basically show you exactly what those are going to look like.
Tim Ulbrich: I think that’s great advice, and the GFE, the good faith estimate to me was kind of the Aha! moment as Jess and I were going through the process. Once you can see that document, you’re like, OK, I can look at this, I can understand it, I can break down all of these costs and you can really start to get that full picture and not just focus on the interest rate, which I think is the common practice when you just get started and you’re getting quotes that are out there. So I love the recommendation of the practice of getting two or three different GFEs from companies, then you can really compare, as Mac’s question, is kind of apples-to-apples. Couple thing that I’ve learned as we’ve gone through this process here over the last month is that I think it’s very easy to just get locked in with a lender really early. And once you’re far enough down that rabbit hole, it’s hard to come back out of it. So I think really starting up front and being clear that you’re getting quotes, get those multiple quotes because I think what we’ve experienced actually on the side of those that are buying our current home is they actually did switch lenders, as Mac’s question is about, can you switch lenders? And how far down the road are you putting things at risk? And the thing you’ve really got to be careful about is that really restarted the whole process and put our sale about two weeks behind. And so you know, documents had to be transferred and how willing is a mortgage company — I mean, how readily available are they going to be to give documents over on a loan they’re no longer doing? And all of these things, and so it can certainly delay the process, so I think shopping up front is really key. And then you can go forward with one lender before you’re too far down the process. To your point, Nate, about the rate lock, I’m actually paying for this right now, this week. So I don’t know if this is something I could have negotiated up front, I think it was one of those things I looked at and said, ‘No big deal. We’re going to close on time, so why does this matter?’ Well, guess what? Closing got delayed, now the rate lock — I’m actually having to pay a few hundred dollars to get an extension on that rate lock.
Nate Hedrick: Yeah, that’s fairly common.
Tim Ulbrich: And I think that if that was something I would have played out and thought, well, what if closing gets delayed? Then I think we could have hopefully prevented that in advance. So great question, Mac. And actually, Mac had a follow-up question via email, unrelated, but on this topic of home buying. He asked, “What should be considered when buying a home to help maximize your tax advantages?” So the dos and don’ts in terms of home buying and tax advantages. And obviously, this is a big question. What are some of your thoughts, Nate, around home buying and tax advantages?
Nate Hedrick: Yeah, that’s a great question. And I’ll try to just hit on a couple of things here because like you said, it is a fairly big question. The first thing I think is important to talk about is what can you do up front? Like what can you do kind of as you’re buying that home to reap some tax benefits? And there are a number of things from, you know, first home buyer tax credits that are available depending on a number of factors. But one of the easiest things you can do is actually — it’s called buying down the rate. And you’ll hear this referred to as mortgage points or buying points. And this is something where if you have extra capital to put into a home purchase, you can actually percentages of that loan to lower your effective interest rate. So if you are buying a $100,000 home, just for easy math, every point on that loan is 1% or $1,000. And every point that you buy, every $1,000 that you spend, drops your interest rate by a certain amount, you know, whether it’s .25% or whatever. So you can put extra money on a loan to effectively lower your interest rate, which is great for the long term, right? If you had that home for 30 years and your interest rate is now a full 1 percentage point lower, let’s say, that’s going to make a big difference over the life of that loan. But in the very next year, basically as soon as you file those taxes for that year that you bought the home, you can also deduct all of that mortgage interest as a deductible on your taxes. So there’s a really cool kind of tax benefit right up front. So that’s one big thing to look at, at least early on. The other thing that you want to look at is — and this is really kind of a thing that’s changed. If you had asked me this question a year ago, it’d be a little bit of a different story. But with the new tax laws, you want to probably know, are you going to be taking the standard deduction next year? Or are you going to be doing the itemized? And with the standard deduction being raised to what it is, a lot of the individual benefits we used to get from homeownership have kind of fallen away. They’re still there, but they’re just not something that you’re going to get any benefit from. The example I have is that basically now that the aggregate amount of state and local sales and property tax is capped at $10,000 a year, people that are buying in New York and California and Hawaii, all these expensive places, they’re not going to see that benefit. You know, you’re no longer really itemizing that deduction anyway. So that cap at $10,000 is not enough to be worth it. So things like that you want to consider: Where am I buying? How am I going to be filing my taxes next year? You know, an accountant can really help with that because that may change your decision a little bit as well. And then the last piece I guess I’ll talk to is that you want to watch for the individual taxes for that area, so the property taxes. And this isn’t something that you can deduct or something that you have to worry about. It is one way to maximize your advantage, right? If I live in a township that has much higher taxes but much better schools, or do I live in a township that has much lower taxes but less amenities and maybe it’s nearby to the things that I want. You know, so that location aspect can be really important as well when talking about tax advantages.
Tim Ulbrich: So Nate, quick question for you on the buying of points, the first tax advantage that you mentioned. You know, I struggled a little bit when I got that offer on the table during the process we’re going through now. And the way I was trying to think about it — and I didn’t think about the deduction side of it, so I’m learning here right alongside the listeners as well — but what I was thinking about it from what’s the break-even point. So if I — just as an example — if I have to spend $2,000 to get my rate down whatever, .4%, you know, I can do the math on that to see that over how many months of saving that interest paid, why recuperate those dollars, and what if I would have just had that cash up front and done something else? So is that the right approach? Or how do you help your buyers evaluate whether or not that purchasing of points is worth it? Or whether those funds could be used elsewhere for other priorities that they’re working on?
Nate Hedrick: Yeah, and that’s a great point. So think about — there’s a couple aspects, and one is how long are you going to be in that home? That’s kind of the first decision. And how long do you expect to pay off that mortgage? If the answer is I can’t wait to buy this down and pay this off in 10 years or less, then buying points is probably not worth it. I think the break-even point is something around the 15-year mark or something like that.
Tim Ulbrich: Yeah, that’s what it was for us. Yep.
Nate Hedrick: Yep. And it varies based on the individual lender, but that’s usually where it’s at. So if you plan on having a true 30-year mortgage, then points can really be worthwhile. But if you plan on buying down your mortgage quickly or paying it off quickly, it’s usually not as beneficial. The other aspect to consider is that as soon as you pay that off, as soon as you put those monies in, it’s harder to get them back out, right? So that money is immediately tied up. So unless you’ve got a real excess of capital, which is obviously harder to find, it may not be worthwhile to tie up that extra money in the property.
Tim Ulbrich: Yeah, I’m especially thinking maybe for some of our listeners that are buying a home, and maybe they don’t yet have a fully funded emergency fund or they have high interest rate credit card debt or other things. So really, it sounds like buying points is an ideal scenario for somebody who is in a great overall financial position, has extra capital, and plans on being in the home for a long period of time.
Nate Hedrick: Yeah, if you’re spending 5% on your student loans every month or every year, you don’t want to be paying, you know, a couple thousand bucks to get a couple of miniscule percentage points off. It’s not worthwhile.
Tim Ulbrich: OK, good stuff. Mac, thanks for your contribution, great questions. Mindy has a question that actually came in via the Real Estate RPH contact form, which is over at YourFinancialPharmacist.com/realestateRPH. She asked, “I’m building a house, second-time home buyer. Wondering what I need to know about the process, things to watch for, etc.” So thoughts for those listeners that may be thinking about building and whether they do or don’t currently own a home, what does that building process bring in terms of new factors and items that people need to be thinking about?
Nate Hedrick: Yeah, yeah. Besides the regular aspects of buying a home, it does add a couple things to the mix. The nice thing is is that you know you’re getting kind of — you know what you’re buying upfront, right? They’re building the home new. You’re not going to find any lagging issues that the home’s been there for 60 years and now the foundation’s starting to crumble, right? As long as everything is done quality upfront, you’re going to get everything brand new, which is a really big advantage. So I think the first question you want to ask if you’re considering building a home is you know, question around the idea of quality. And I think you don’t want to go to them and say, ‘How nice are your homes? Like what’s your quality?’ Like that doesn’t tell you anything because they’re just going to say, ‘They’re fantastic.’ And then you’ve learned nothing. But you want to ask some pointed questions, you know, things like, ‘Talk to me about some of your building standards. Talk to me about how energy-efficient your homes are.’ Because those are things that are going to show you yes, they follow code, but how close do they get to modern building standards? How close do they get to really high energy efficiency standards because those are much more better indicators of quality than just, oh yeah, we always follow code. Like you wouldn’t be a home builder if you didn’t follow code. So asking the right quality questions is a really good place to start, and that will help you know that what you’re getting when you put all that money in is going to be worthwhile. The second part is really the additions or the amendments or the kind of the perks, right? So you’re going to sit down when you’re building a home, and they’re going to walk you through and they’re going to say, ‘OK, the base model that you’ve selected is $400,000. Now let’s get to some of the upgrades.’ And these upgrades can take you — I’ve seen them honestly double the price of a home from that base value. So be careful when they say, ‘starting in the $300s.’
Tim Ulbrich: Starting at…
Nate Hedrick: Yeah, exactly. Like you’ll see that advertised on the big signs for the new developments. ‘Starting in the $200s,’ and realistically, no one’s walking out of there for under $300,000. So the upgrades, the things I would caution you on or draw your attention to is that take the upgrades that you find beneficial. Don’t let them talk you into things that, oh, this ups the resale value. So if you sell this home in five years, this is what people are going to want. If you’re building a home, in all likelihood, you’re building it for you. And so you should buy the upgrades that you want. One of the things I just had a client walk into it and was working through is that they said, ‘Well, we can do your upgraded kitchen cabinets. And right now, the popular thing is to do dark cabinets on the bottom and light cabinets on the top. And that’s only going to be $10,000 more, and you get this super modern kitchen.’ Well, if they sell that home in 10 years and that’s not popular, they may have to redo that. So if you don’t want that, don’t buy it. And that’s I think a good addage for all the upgrades that go with building a home. If you don’t want it, don’t invest that money because you’re the one that you’re building it for.
Tim Ulbrich: So Nate, one of the things that I’ve always wondered about building a house — we’ve never been through the process — is how does the cash flow needed differ from a buying a existing home? So if I’m in a current home, and I’m looking at building, how does that work in terms of selling and the timing? Am I having to put down money earlier where I necessarily can’t wait until the sale of my home? Or is it very similar to buying an existing home that those things are all ironed out?
Nate Hedrick: Yeah, it’s a little different because a lot of times, you have to buy the lot or you have to put in some sort of down payment to secure the lot. And sometimes, you have to buy the lot like upfront. Like it’s a $28,000 or a $50,000 piece of land that you have to basically buy upfront, and then you move forward. Or sometimes they can say, ‘OK, well it’s a $50,000 plot. We need $5,000 to secure this.’ But generally, it’s a lot more. It’s usually on the higher end of securing that location. So depends on the popularity, it depends on how they want to structure it. But there’s really two sides to it. One is basically securing that land and buying that land, and then the second is getting the mortgage on the home itself. And you can often wrap those things together so that everything’s kind of one piece, but the builder and the developer usually wants a lot more upfront to secure that property to begin with.
Tim Ulbrich: You know, one of the things that I’ve seen in our neighborhood, and we don’t actually have a homeowners association, so this may be different in areas that have a little bit tighter regulations, but we’ve actually seen several houses go up where my guess is maybe they didn’t anticipate all costs involved where six or 12 months later, like the yard is still not in or something’s not fully finished, you know, in terms of a porch or something else. So I think just things to consider, to your point earlier about, you know, what is the starting out price? What’s the actual price? And going back to you really defining your budget before you go into those conversations with the builders or else I think it easily could be a conversation where you start at $250,000 and you end at $400,000, you know, depending on what you’re looking at. So Lauren via the Facebook group asked, “What are your thoughts about real estate crowdfunding sites like FundRise?” So talk to us a little about what are real estate crowdfunding sites and what are your recommendations on these for those that may be interested in doing some real estate investing?
Nate Hedrick: Yeah, this was an awesome question from Lauren. I actually answered it on the Facebook page because I’m in the middle of writing an article about it right now. My wife Kristin actually found FundRise — I had never heard of it before — and said, ‘What is this? Like what’s going on with this?’ And I said, ‘I’m going to find out.’ So I’m actually in the middle of writing this article right now because it’s super interesting. The basics is this: So it’s a REIT, which is Real Estate Investment Trust, but they’re calling it an e-REIT, or an electronic or online or whatever they want to define it as. But the idea is very simple. The idea is that they’re a group of individuals who buy real estate — and this is many aspects. They’re buying rental properties, they’re buying commercial development, they’re buying land, they’re buying all sorts of stuff. And you yourself wouldn’t be able to buy those pieces, you wouldn’t be able to buy the land, you wouldn’t be able to buy the commercial buildings, but if you could buy a very, very small chunk of that, you could still reap some of the benefits. So if you put in, you know, a couple thousand dollars, and 50 people do that, now all of a sudden, they’ve got the capital they need to go forward and take on these big investment and real estate investment properties and projects. So you’re basically crowdfunding a investor group to do these things. So it’s kind of like a mutual fund where you’re buying small chunks of a larger company, but instead, you’re buying small chunks of a larger real estate investing group. And I’ll say a couple of things about FundRise in particular. And I don’t have any personal experience investing with them, so I’ll say that upfront, but the reading that I’ve done and looking through their fine print, I think there’s a couple of aspects. One is that I think that their model is very good in terms of what they’re investing in, where they’re doing it. I think they’re a little ahead of the game. They’re kind of targeting areas that are still not quite on the rise but will be on the rise soon. So I think they have good investments. People in the industry that are talking about them, they’re investing in the right areas. And their current return on investments in the 10-12% area are indicators that they’re doing the right things. So that’s a good sign, right? That they’re investing in the right areas. The problems I think come in when you look at how that money that you’re giving them is being used and how you get it back. They are not a publicly traded entity. They are a publicly available entity. And those are two very different things. If I go into my brokerage account and buy a REIT, a buy a portion of an investing property, I can sell that at any time. It’s publicly traded, so a broker will take that off my hands as soon as I am ready to sell it. Just like a stock — if I buy Apple stock and then go sell it tomorrow, someone’s going to buy that. That’s publicly traded. But if it’s publicly available, I may not have someone available to buy that investment whenever I need to sell. So I could say, ‘Hey guys, I want to cash out. I’m done with FundRise. I want my money back,’ and they would be like, ‘Well, nobody’s buying right now at the price you’re offering. So I’m sorry, we ahve to hold onto your money.’ And if you read all the fine print, they actually really talk about how illiquid the money really is. They can hold onto your money almost indefinitely if it benefits the group of investors. And really, I want you guys to look at that on your own terms because it’s pretty interesting to see how that breaks down. But the idea is simply that if they find it to be in the best interests of the investor group, they can hold onto that money for a long period of time, so it’s pretty difficult —
Tim Ulbrich: That’s interesting.
Nate Hedrick: Yeah, it can be difficult to get that money back out. And I’m sure people are — right now, at least it’s fine. But who knows what it’s going to look like five years down the road? So that’s one of the big concerns that I have. The other one is that even though there have been great returns — and again, 10-12% is fantastic returns for something like this — their fee structure is a little bit high. They talk about only charging about 1% upfront, but if you really break down the fees that are built into the back end, fees can be upwards of 3% a year. So the fees can be quite high, and that’s something that you really want to take into account because that’s taking away from your gains. So all of a sudden your 12% is down to 9%, and if they start dropping and they go to 8-10%, now you’re talking about gains that are less than the S&P. And so is it really worthwhile to have this illiquid money making less than you make in a general just brokerage account. So there’s a couple of pieces to consider there.
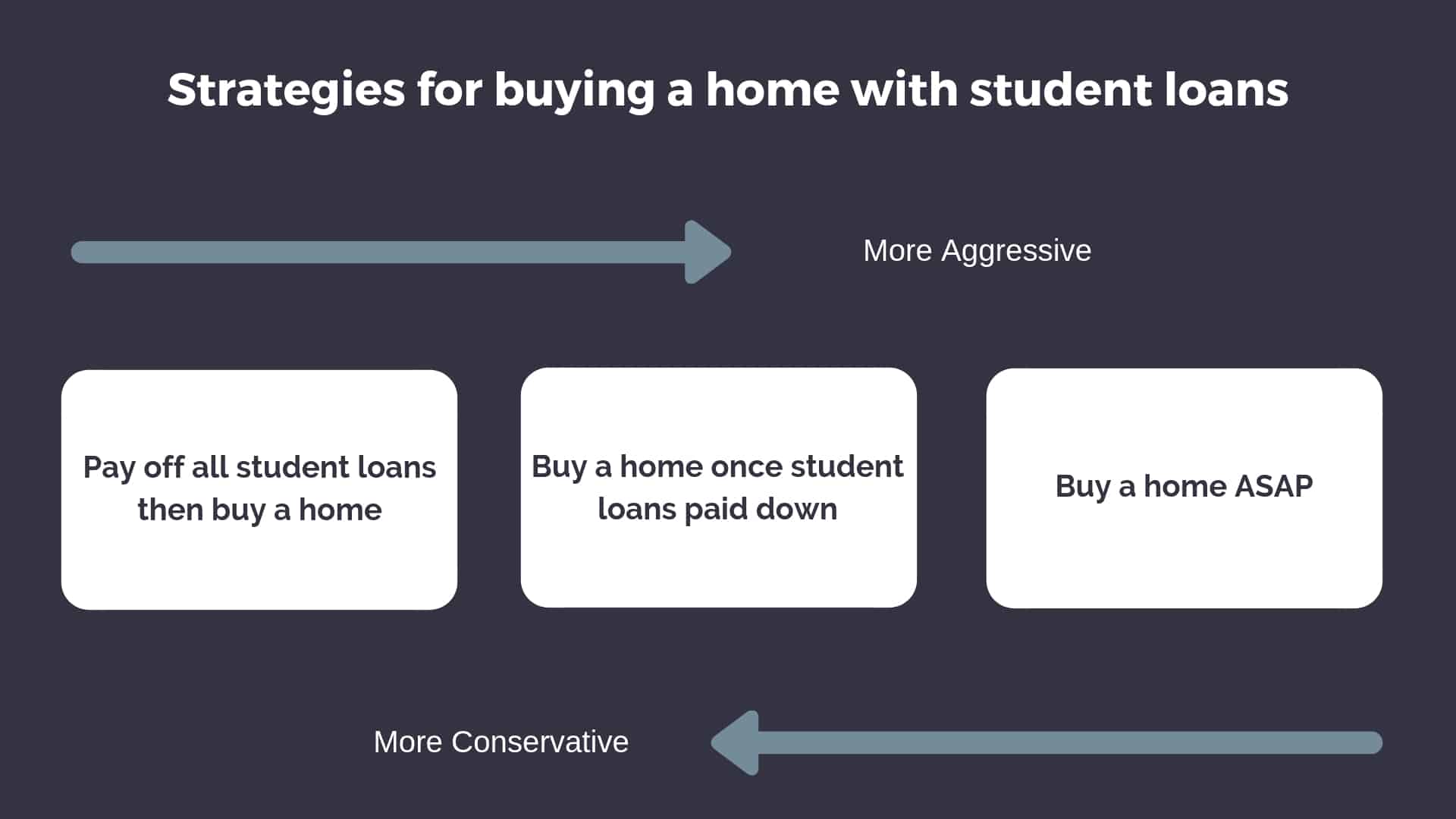
Tim Ulbrich: Yeah, those are great points. And I would encourage to our listeners that are thinking about this, don’t forget about your tax advantage retirement savings account. So your 401k’s, 403b’s, Roth IRAs, obviously there’s inherent tax benefits of being involved in those accounts that you may not see with something like a FundRise. So don’t forget to factor that into the equation. And certainly I know in my 401 account, I certainly have the option to invest in REITs, and so is there a way that you can get involved in diversifying your investments into real estate while still taking advantage of those tax advantage retirement accounts if you’re not already doing so. Couple other questions that I want to throw out there briefly because I think they’re ones that I get often. The first one is, Nate, probably the most common question I get. And I was surprised we didn’t get it on the Facebook group is, where does home buying fit in with student loan debt? So is buying a home appropriate when I have $150,000-200,000 of student loan debt? If so, is there an ideal or a right time? And what are some of the principles I should be thinking about? And so I wanted to get your thoughts on this one.
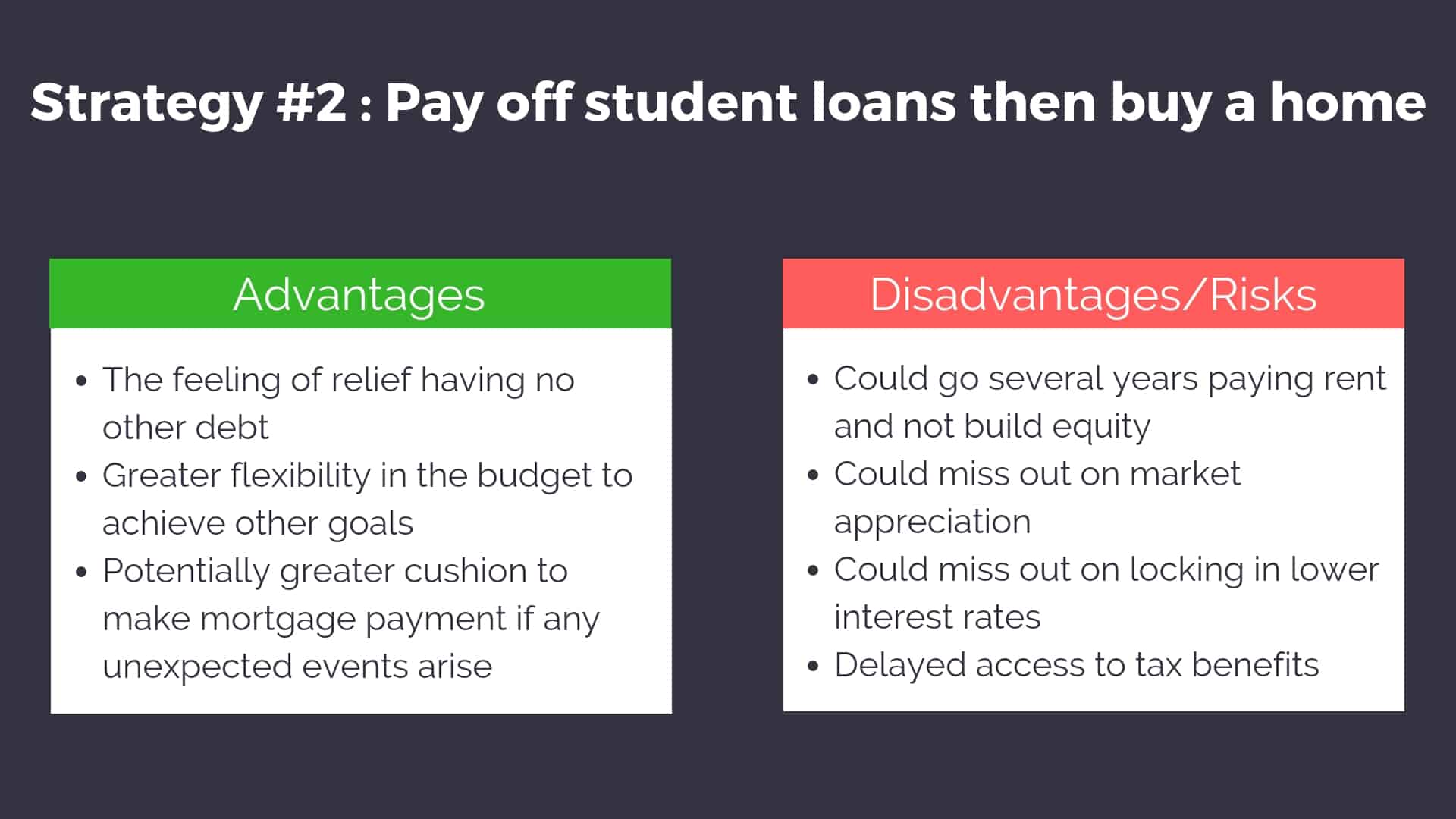
Nate Hedrick: Yeah, it’s a great question. It’s actually a really large question. And I think the simplest answer is it fits in wherever your priorities say it does. And that’s almost too simple of an answer, but it really is the truth. If you need a home right now. If your family or your personal environment says that I need a home right now, then you’re going to make it work with your student loan debt. It’s certainly possible. If you are someone that just hates being in debt and hates the idea of owing somebody more than your salary, you’re probably going to wait. You’re going to pay off those loans first before tackling the home buying process. But it really depends on that priority set. In fact, Tim Church and I — Your Financial Pharmacist Tim Church and I have been working on an article that will be coming out probably around the time this podcast is launched. It talks all about how to buy a home with student loans and what that can look like. So it really comes down to your personal journey and where you’re at and trying to fit that in. I mean, I’ll be honest. I’ll tell you, when my wife and I bought our home, we were well into the negatives in our net worth at the time. But it was something that for us, we wanted a home, we needed a home at the time. So it was worth doing. And it really depends on your own situation.
Tim Ulbrich: Yeah, Jess and I were right there with you. And I think for me, this is such a personal, customized question that the answer to this is different for everyone, right? So you know, I think this is a great example of sitting down and really looking at all of your financial goals in terms of things we’ve talked about before on this podcast: emergency funds and how much debt? And is there credit card debt? And where are you at with retirement savings? And what other financial priorities are on the table? And I think the thing I would encourage the listeners to think about is on a month-to-month basis, depending on your student loan payment, as you look at evaluating the home purchase, you know, you really want to be cautious and not put yourself in a situation where you feel like between your student loan payment and your mortgage payment, you really got no margin to do anything else or a little margin where you’re feeling super stressed each and every month. Now, that can also be tricky because some people may say, ‘Well, I’ll opt into income-driven repayment plan, I’ll minimize my student loan payment, I’ll free up cash, and I’ll then be able to purchase a home.’ But obviously, that has limitations as well, being in student loan debt longer. So I think really taking a step back, working with a financial planner like Tim Baker or really looking at all of your financial goals to say, ‘OK. Where does home buying fit in with all these other priorities?’ And then if it fits in at this point in time, what’s the best next step in terms of how much down, what’s the overall purchase price of the home, location, all of the other factors we’ve been talking about this entire month. Nate, one last question I have here. We’ve gotten a lot of action in the YFP community about real estate investing. And I think there’s a big interest out there, rightfully so, especially while the market’s hot, of course. But we had Carrie Carlton on in Episode 009 that talked about real estate investing, which is one of our most popular episodes. For those that haven’t listened to that, I would check that out. But I think many people are thinking about, OK, where is the job market heading? You know, I want to think about an alternative revenue stream. Real estate investing may be that alternative revenue stream. So for those that are thinking about investing in real estate, whether that be for a side income, a business, diversification of investments, what is the best first step they can take? And I think with other financial priorities also in mind, such as emergency funds, debt, etc., is there a right time to jump into real estate investing? So I know this is a huge question. We could do a separate series in episodes, we probably will in the future. But I know we have listeners that are thinking about real estate investing. I want to give them something to hang onto as the next step. What do you think?
Nate Hedrick: Yeah, no, I think that’s great. And you’re right, it’s a huge question. This is why I have a website, right? This is why I have the Real Estate RPH because this is exactly where I was. I remember reading “Rich Dad, Poor Dad,” learning about passive income and real estate investing and thinking, how do I jump into this? What’s the next step I can take? So if you’re looking for the next step, I think the very first thing you should do no matter what is educate yourself. Listening to podcasts like this, checking out blog posts for our site and for Real Estate RPH, that can be a really great tool. And there are so many other resources out there. There are books, there are blogs, there are podcasts. But educating yourself about the types of investing can be a really great first or next step. And then once you’ve done that, and if you want to take a tangible action, you know, I want to do something and see what this actually looks like, I really encourage people to assess some deals in the area that you’re considering. I work with a lot of pharmacist investors here in Cleveland, and the very first thing if they’re new investors, they say, ‘Well, where do I start? What do I do?’ I say, ‘Well, I need you to assess some deals first. Understand the market in which you’re looking in so that you know what a good deal looks like.’ And there are a number of tools that can help you do this. But really, the best thing is just go pen and paper and a calculator. But seriously looking at what available homes are there on the market right now? What are rents looking like if I’m going to rent that? Or what are flips looking like? Or comps looking like if I were to flip that home, depending on the type of investing you’re going to do? And just figure out if that is a good deal, a bad deal or something in between. And then once you have that pulse on the market and you understand it and you’re doing the education and the background, it becomes that much easier when a good deal comes along, you can actually pull that trigger and look at seriously putting an offer on that home.
Tim Ulbrich: So for me here, I think it’s all about learning. Reading, blog posts, books, listening to podcasts, engaging in communities like this one. And I love your advice of really looking at deals and doing the math on them. And I think when I think about real estate investing, Nate, I think all of us have either a family member or a friend or somebody who’s doing this and who is encouraging us to get involved in real estate investing and talks about all the upside of real estate investing. And of all the things I’ve read, for every good, positive return on investment story when it comes to buying homes, there’s probably five that have gone bad that maybe you’re not going to hear about. So really doing your homework, doing the math, making sure you understand all of the costs, everything involved. But we’ll definitely have more content coming on this topic in the future, so stay tuned in the YFP blog, podcast and Facebook group as well. So Nate, this month has been a ton of fun. We are super excited about the partnership between YFP and Real Estate RPH. So thank you so much for taking the time to come on the podcast, contributing to the blog. And for our listeners, again, we continue to bring you content around real estate investing, buying and selling homes. If you have a question that you’d like to get answered by Nate, head on over to YourFinancialPharmacist.com/realestateRPH, and Nate will get back to you in regards to your question. As we wrap up today’s episode of the Your Financial Pharmacist podcast, I want to take a moment to again thank our sponsor, Splash Financial.
Sponsor: If you’re looking to refinance your student loans, head on over to SplashFinancial.com/YourFinancialPharmacist, where in just a few minutes, you can check your rate. Splash’s new rates are as low as 3.25% fixed APR, which can literally save you tens of thousands of dollars over the life of your loans. Plus, YFP readers receive a $500 welcome bonus for refinancing with Splash. Again, that’s SplashFinancial.com/YourFinancialPharmacist.
Tim Ulbrich: Hey, thank you so much for joining me for this week’s episode of the Your Financial Pharmacist podcast. Next week, Tim Baker and I will be talking about the pros and cons of Dave Ramsey’s seven baby steps and how they do and don’t apply to the pharmacy profession. This is a good one, you’re not going to want to miss this episode. If you’ve liked what you’ve heard on this week’s episode, please make sure to subscribe in iTunes or wherever you listen to your podcasts. Also, make sure to head on over to YourFinancialPharmacist.com, where you’ll find a wide array of resources designed specifically for you, the pharmacy professional, to help you on the path toward achieving financial freedom. Have a great rest of your week.
Join the YFP Community!
Recent Posts
[pt_view id=”f651872qnv”]























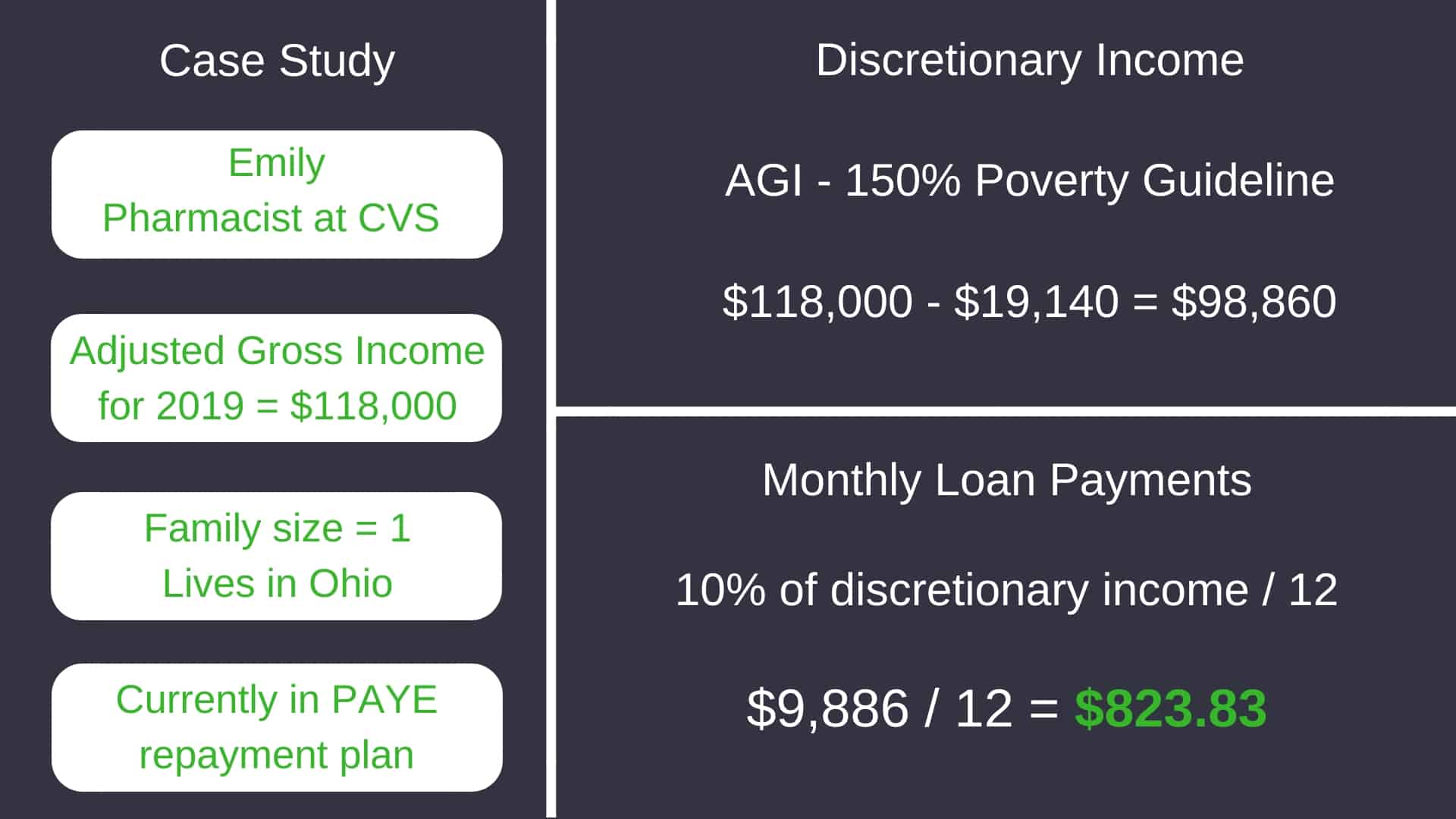
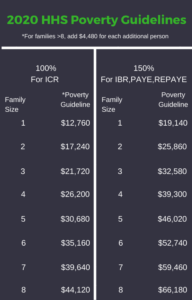 The specific income driven repayment plan will determine what percentage of the poverty guidelines is used in the calculation. For most plans including Pay-as-you earn (PAYE), Revised pay-as-you-earn (REPAYE), and Income-based repayment (IBR), it is 150%. For Income contingent repayment (ICR), it’s 100%.
The specific income driven repayment plan will determine what percentage of the poverty guidelines is used in the calculation. For most plans including Pay-as-you earn (PAYE), Revised pay-as-you-earn (REPAYE), and Income-based repayment (IBR), it is 150%. For Income contingent repayment (ICR), it’s 100%.